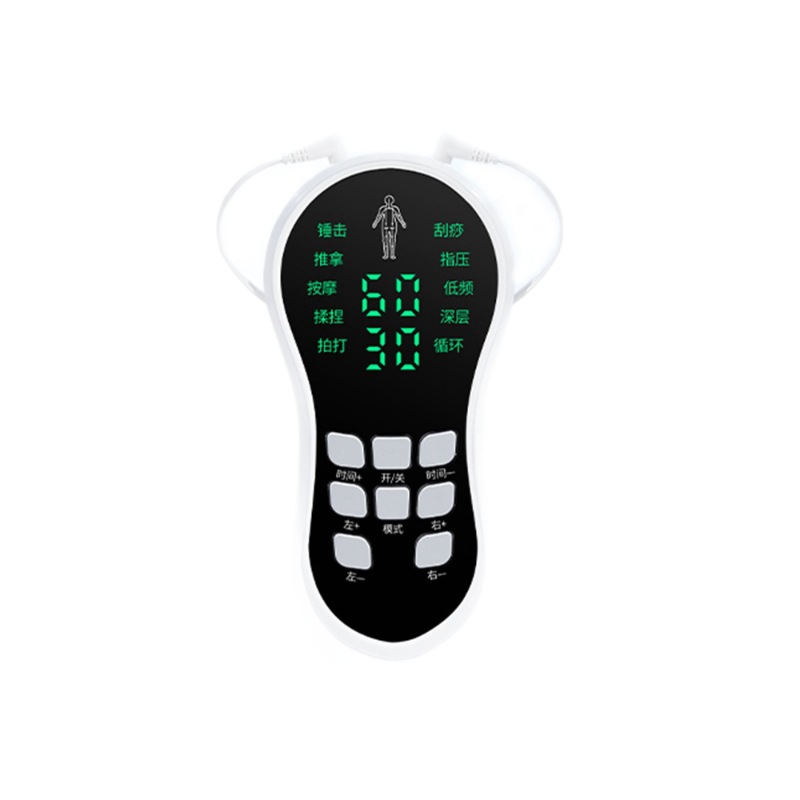
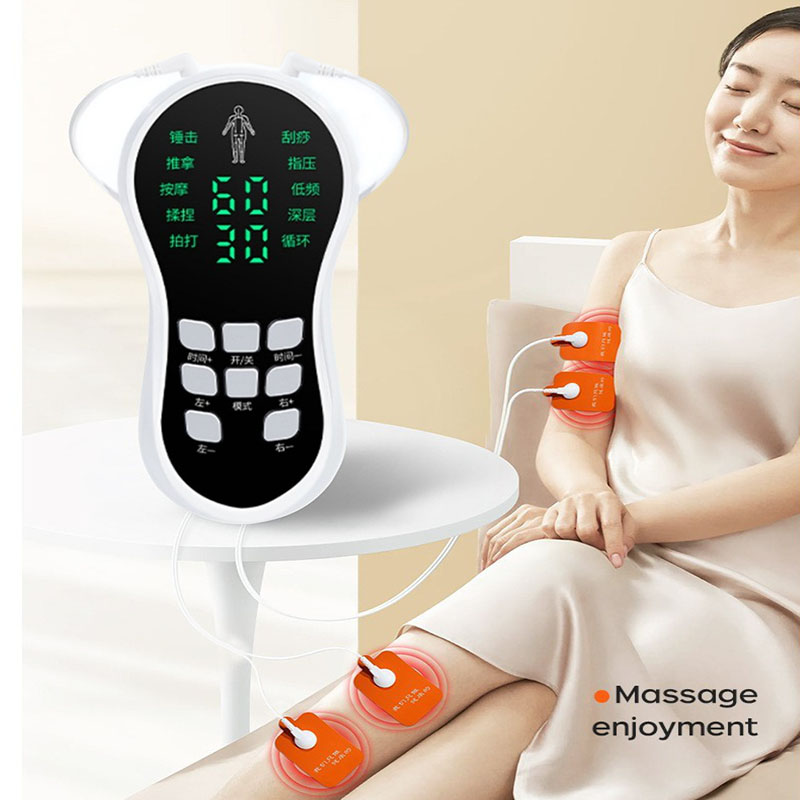
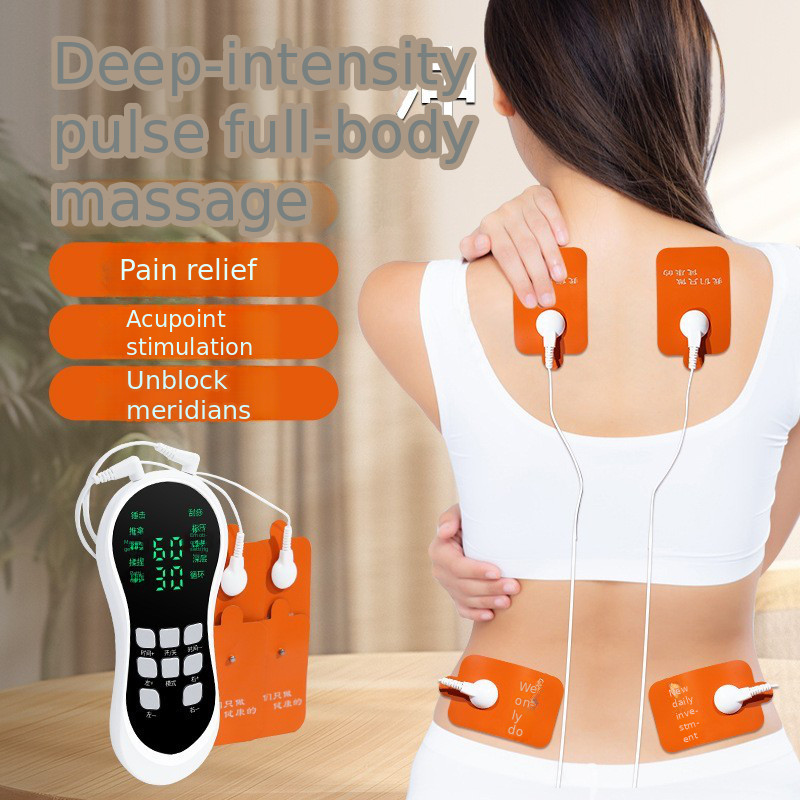
What does a TENS EMS unit do?
You're dealing with both nagging pain and muscle weakness. Buying separate devices is costly and inconvenient. A combined TENS EMS unit offers a single, powerful solution for both problems.
A TENS EMS unit is a two-in-one device for pain relief and muscle conditioning. The TENS mode blocks pain signals for drug-free relief, while the EMS mode stimulates muscles to aid in recovery, rehabilitation, and training.
I’ve been in the personal care device industry for a long time, from the factory floor to running my own company. I’ve seen these combination units become incredibly popular, and for good reason. They offer a huge amount of value. For my business partners, whether they run a wellness center or a retail chain, understanding this versatility is key to helping their customers. Let's get into what these powerful little devices can really do.
What is the difference between a TENS unit and a tens ems unit?
You see all these different devices on the market. It's confusing trying to figure out if you need just TENS, or if this combo TENS EMS unit is better for you.
A standard TENS unit is a dedicated pain relief device. A TENS EMS unit is a multi-function tool that includes both TENS for blocking pain signals and EMS for stimulating muscle contractions, making it more versatile for overall recovery.

When I work with international distributors, this is the first thing we clarify. The distinction is simple but crucial. A customer who only has pain might be fine with a basic TENS unit. But a customer who is an athlete, recovering from injury, or looking to maintain muscle tone needs more. The combo unit serves both needs. Think of it this way:
TENS vs. EMS: Two Jobs, One Device
| Function | TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) | EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Sensory Nerves | Muscles |
| Purpose | Pain Relief (blocks pain signals) | Muscle Contraction (rehab, training) |
| Sensation | Gentle tingling or buzzing | Rhythmic muscle twitching |
From a business perspective, offering a 2-in-1 device is smart. For a retailer, it streamlines inventory. For a spa or fitness club, it provides a broader range of services with a single piece of equipment. It offers a more complete wellness solution, which is exactly what today's educated consumer is looking for.
Do TENS and EMS really work?
With so many gadgets promising quick fixes, it's right to be skeptical. You want to know if putting pads on your skin and sending electricity through them is actually effective.
Yes, both TENS and EMS are scientifically-backed technologies that work when used correctly for their intended purpose. TENS is a proven method for short-term pain relief, and EMS is a staple in physical therapy and sports medicine for muscle rehabilitation.
The science behind them is solid. TENS works on what’s called the "Gate Control Theory of Pain." The gentle electrical signals essentially distract the nerves, closing the "gate" that would normally let pain signals travel to your brain. It’s effective, but it’s a temporary fix; it manages the symptom, not the cause. EMS, on the other hand, mimics the signals your brain sends to make your muscles contract. This is incredibly useful in physical therapy, where a patient might not be able to actively contract a muscle after surgery. It helps wake the muscle up. I always stress this to my partners: be honest about what the device can do. It's a powerful tool, not a miracle cure. TENS provides fantastic temporary pain relief. EMS is a great aid in rehabilitation but won't build a six-pack on its own. It has to be used with an active lifestyle.
What does an EMS unit do for muscles?
You hear that an EMS unit can "work out" your muscles for you. It sounds too good to be true. How can a device build or relax muscles without any effort?
An EMS unit causes passive muscle contractions. It sends signals that make your muscles tighten and relax, which helps prevent atrophy, improves local circulation, assists in post-injury rehabilitation, and can be a supplement to active exercise.
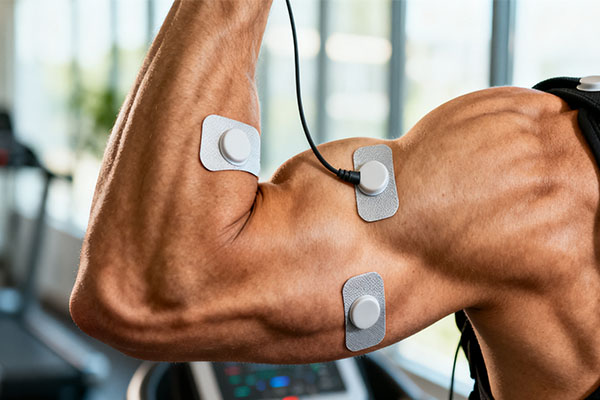

When I explain this to fitness club managers, I describe EMS as a "personal assistant" for your muscles. It doesn't replace the hard work of exercise, but it plays a crucial supporting role. For example, after a major surgery, a person's brain-to-muscle connection can be weak. EMS helps re-establish that pathway by forcing the muscle to contract, reminding it what to do. This prevents muscle wasting (atrophy), which is a huge problem for anyone who is immobilized. For healthy athletes, using EMS after a hard workout can help with recovery by increasing blood flow to the area. It can also be used to target small, stabilizing muscles that are hard to work in a traditional gym session. It's a precision tool. It creates a real, physical contraction, but its greatest strength lies in rehabilitation and recovery, not in replacing your workout routine.
How often should you use an EMS muscle stimulator?
You feel the EMS working, and you're motivated to get results fast. You might be tempted to use it every day, but this approach can actually backfire and slow down your progress.
You should use an EMS muscle stimulator on the same muscle group only 2-3 times per week. Your muscles need adequate time to recover and rebuild, just like with traditional exercise. Constant stimulation leads to fatigue, not growth.

This is one of the most important safety and efficacy points I emphasize. I always compare it to weightlifting. You wouldn't go to the gym and train your legs with heavy squats every single day, would you? Of course not. Your muscles get stronger during the rest period after the workout. EMS is no different. The stimulation creates micro-tears in the muscle fibers, and they need time to repair and come back stronger. If you stimulate them constantly, you're just breaking them down without giving them a chance to recover. This can lead to excessive fatigue, soreness, and even injury. For my clients who are home healthcare retail buyers, providing these clear instructions is non-negotiable. Customers need to know that a 20-minute session, followed by a day or two of rest for that muscle group, is the safe and effective way to get results.
Conclusion
A TENS EMS unit is a versatile tool for pain relief and muscle support. Use TENS for pain and EMS for muscle recovery, but always allow your body adequate rest.